 Weitzner
WeitznerInformation Accountability
 Weitzner
Weitzner21 June 2007
Semgrail Workshop
Microsoft Research
Redmond, WA
Daniel J. Weitzner
Decentralized Information
Group
MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
These slides: http://dig.csail.mit.edu/2007/Talks/0621-info-account/
 |
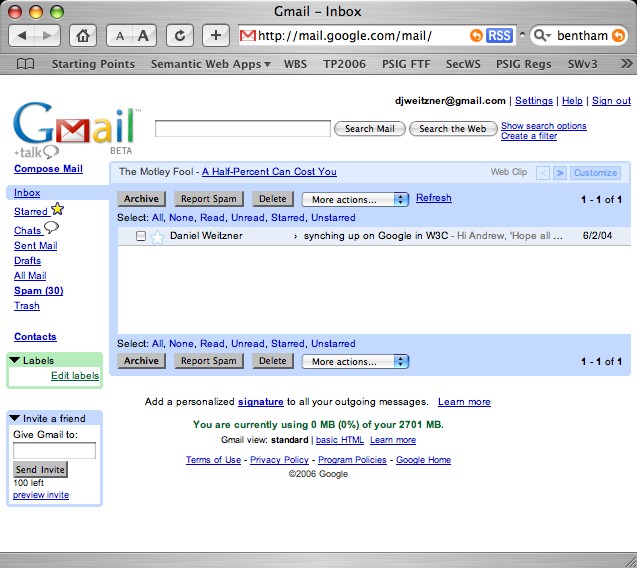 |
We learn that what people care about is how information is used, not who has access to it.
Saltzer and Schroeder, The Protection of Information in Computer Systems:
"The term 'privacy' denotes a socially defined ability of an individual (or organization) to determine whether, when, and to whom personal (or organizational) information is to be released."
Communications of the ACM 17, 7 (July 1974).
Goal: construct data base protocol that limits information access according to a formal definition of privacy
Privacy Definition: indistinguishability of the individual from the community
Method: measures epsilon-indistinguishability of a database query transcript
Differential Privacy, Cynthia Dwork, 33rd International Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Programming, ICALP 2006, Part II, pp. 1–12, 2006.
see also Sweeney's k-anonymity work
A privacy-safe zone: Privacy sensitive data mining establishes a boundary, which, if respected, assures no privacy risk to the individual.
 |
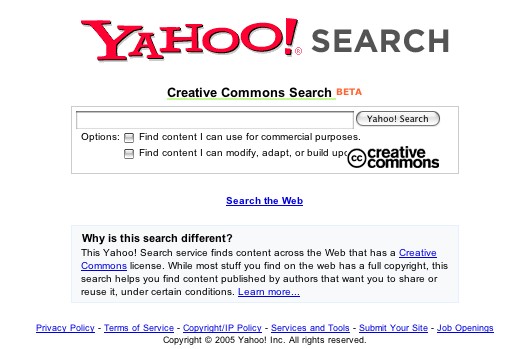 |
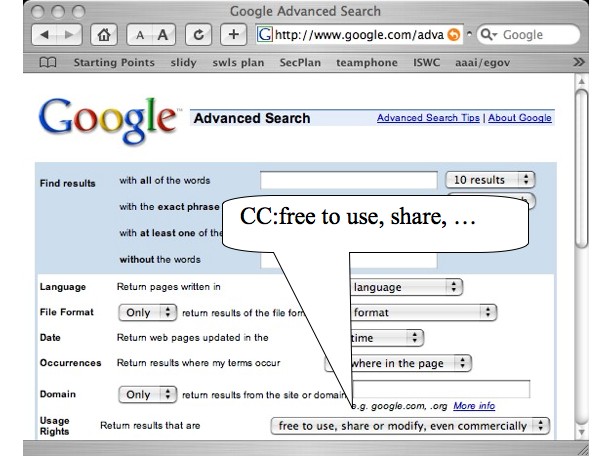
Move from up-front enforcement barriers (DRM) -> open description of licensing terms (CC) with after-the-fact enforcement as needed
 |
"Imagine a world where every online store sells DRM-free music encoded in open licensable formats. In such a world, any player can play music purchased from any store, and any store can sell music which is playable on all players. This is clearly the best alternative for consumers, and Apple would embrace it in a heartbeat. If the big four music companies would license Apple their music without the requirement that it be protected with a DRM, we would switch to selling only DRM-free music on our iTunes store. Every iPod ever made will play this DRM-free music," Steve Jobs, Thoughts on Music (February 6, 2007) |
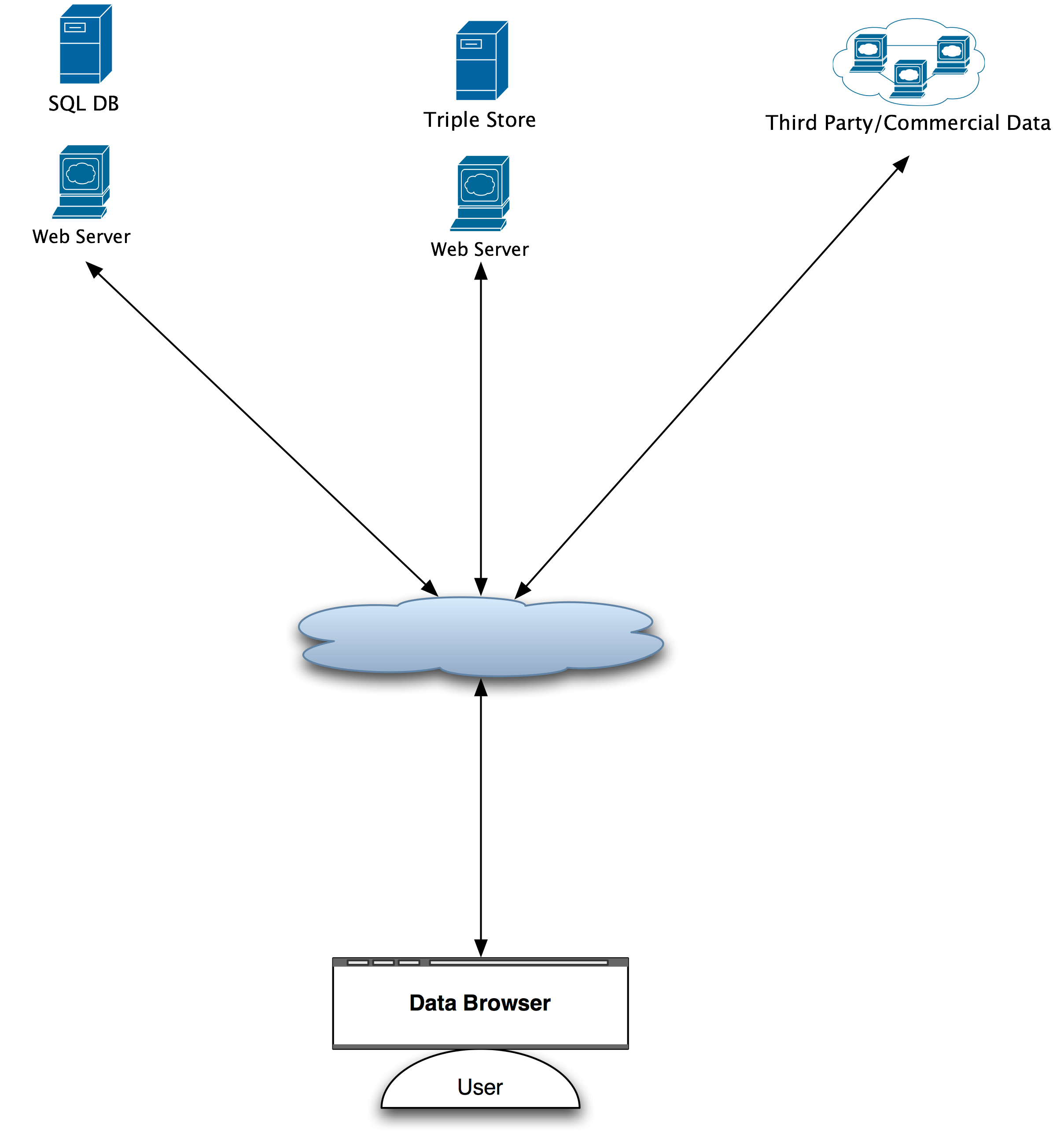
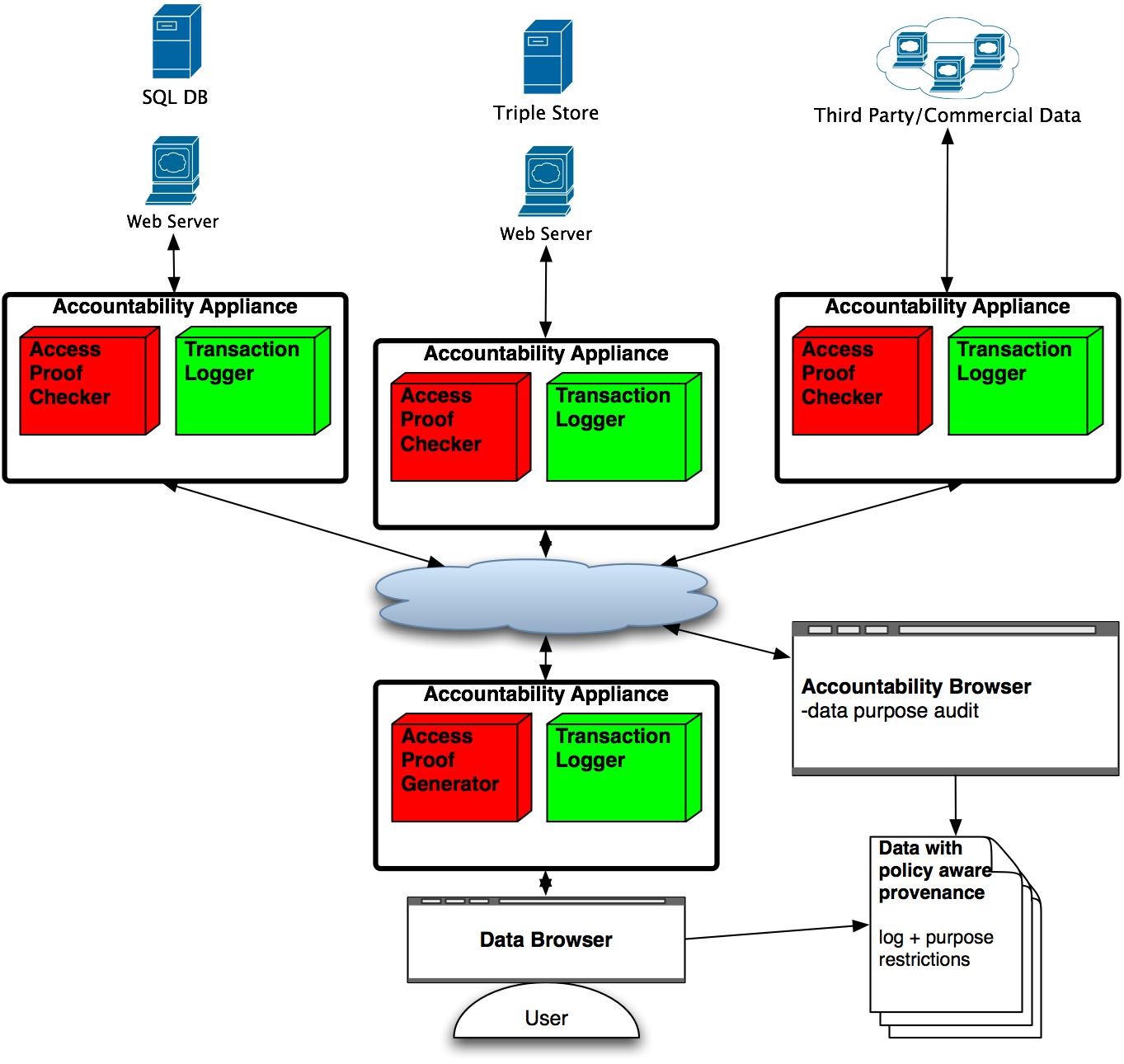
|
|
Web has changed our relationship to information
Controlling information flow will no longer suffice to ensure adherence to policy
Goal -- new systems that support accountability to policy rules
For more information see:
Work described here is supported by the US National Science Foundation Cybertrust Program (05-518) and ITR Program (04-012).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 2.5 License.