Varying the levels of explanation within a generic RDF data browsing environment
Oshani Seneviratne
CSAIL Student Workshop
22 September 2008
Overview
- What is a generic RDF data browser?
- What are varying levels of explanation?
- An Example
Generic RDF Data Browsers?
Tabulator
- Available in Firefox Extension and Online flavors
- Avoids RDF jargon in your face
- Looks up data on the web and follows links
- Can do SPARQL Queries
- Can Modify exising and Add new data
- Can be customized for application specific tasks
Varying Levels of Explanation?
Different Views

- About the Document
- Under the Hood
- Data View
- RDF/N3 View
- RDF/XML View
- Explanations View
- Lawyer's View
- Friend-Of-A-Friend View
Panes
Example Applications
- Open Social Network Based on FOAF Data
- Justification User Interface
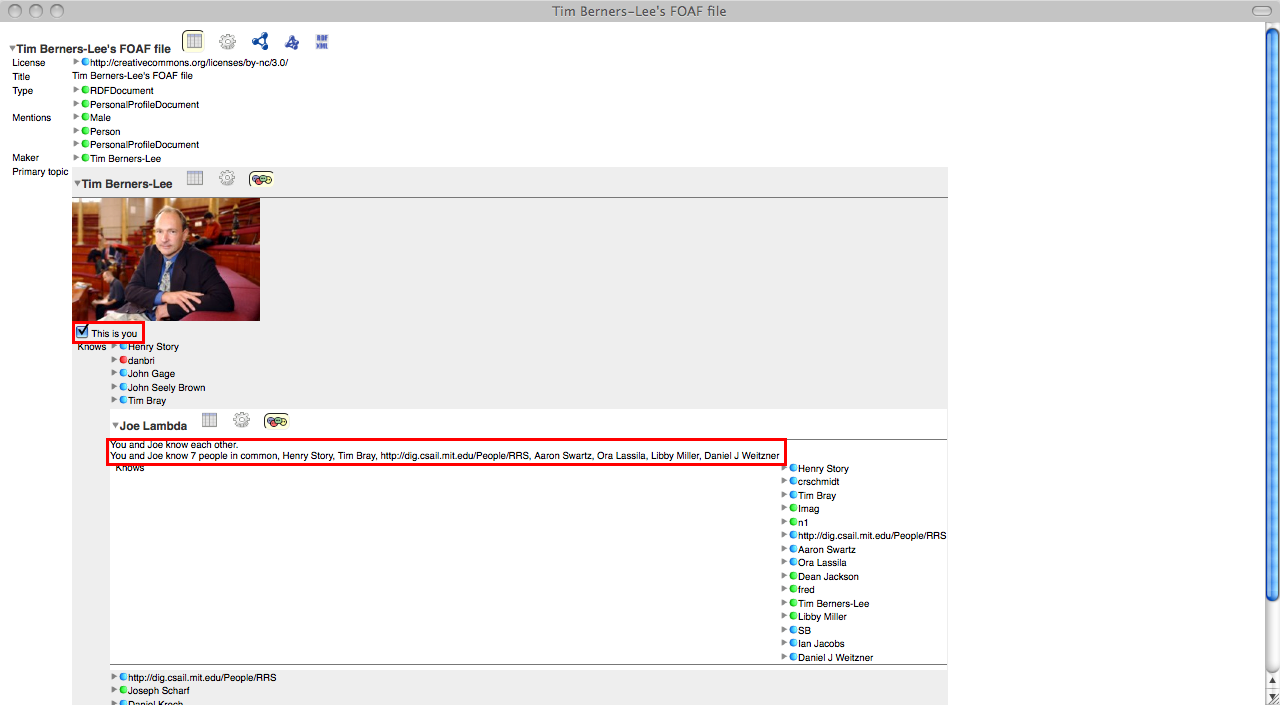
Open Social Network Based on FOAF Data
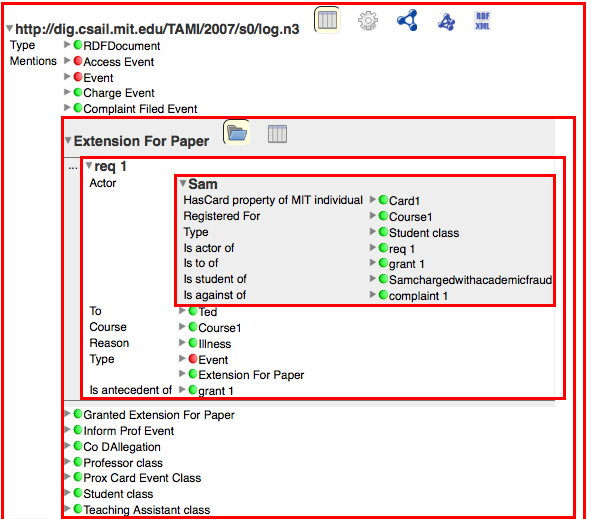
Justification User Interface
Scenario
Transactions
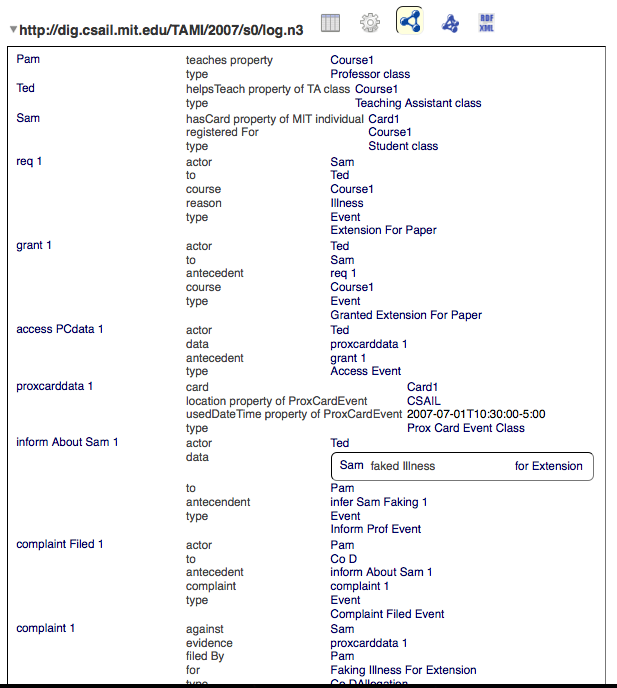
- On Monday at 9am Student Sam is granted extension on paper due to illness based on claim that she is sick in bed.
- An entry in the CSAIL prox card log shows Sam entering 5th floor of CSAIL at 9:45am/Monday.
- TA Ted looks at prox card log and discovers that Sam was in CSAIL.
- Ted tells Professor Pam who files a compliant with the CoD.
- CoD hearings are not criminal proceedings.
- CoD hearing calls Sam to explain and presents a machine-readable complaint citing entry in prox card log as evidence that she lied about matters of academic significance.
Scenario
Transactions
Scenario
Policy
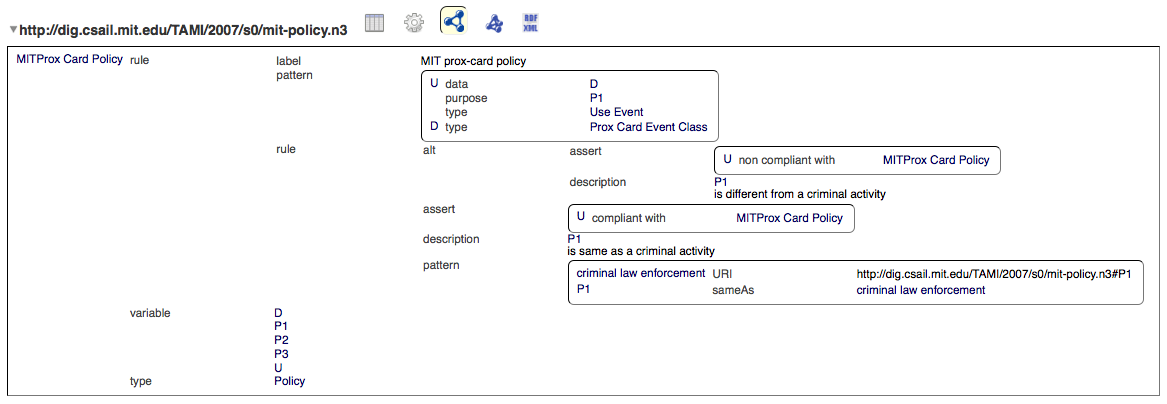
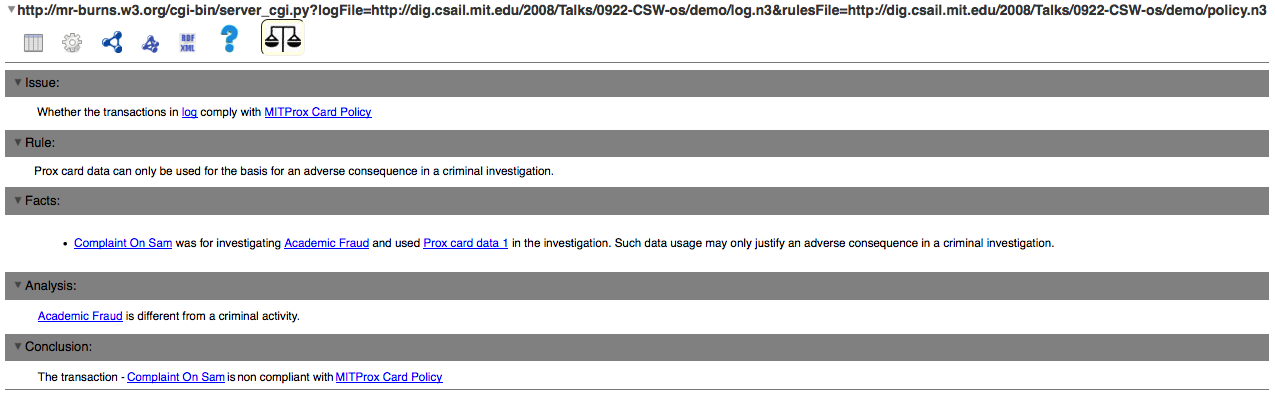
- Assume that the MIT Prox Card Data Policy states that prox card data can only be used for the basis for an adverse consequence in a criminal investigation.
Scenario
Policy
Scenario
Outcome
- Accusation of lying by the CoD against Sam cannot be supported by the available facts
- Argument in complaint is invalid because:
- Accusation is of lying
- Lying accusation is supported by prox card data
- Prox card data may only justify an adverse consequence in a criminal investigation
- Therefore, the accusation on Sam is non-compliant with the policy.
Scenario
Outcome
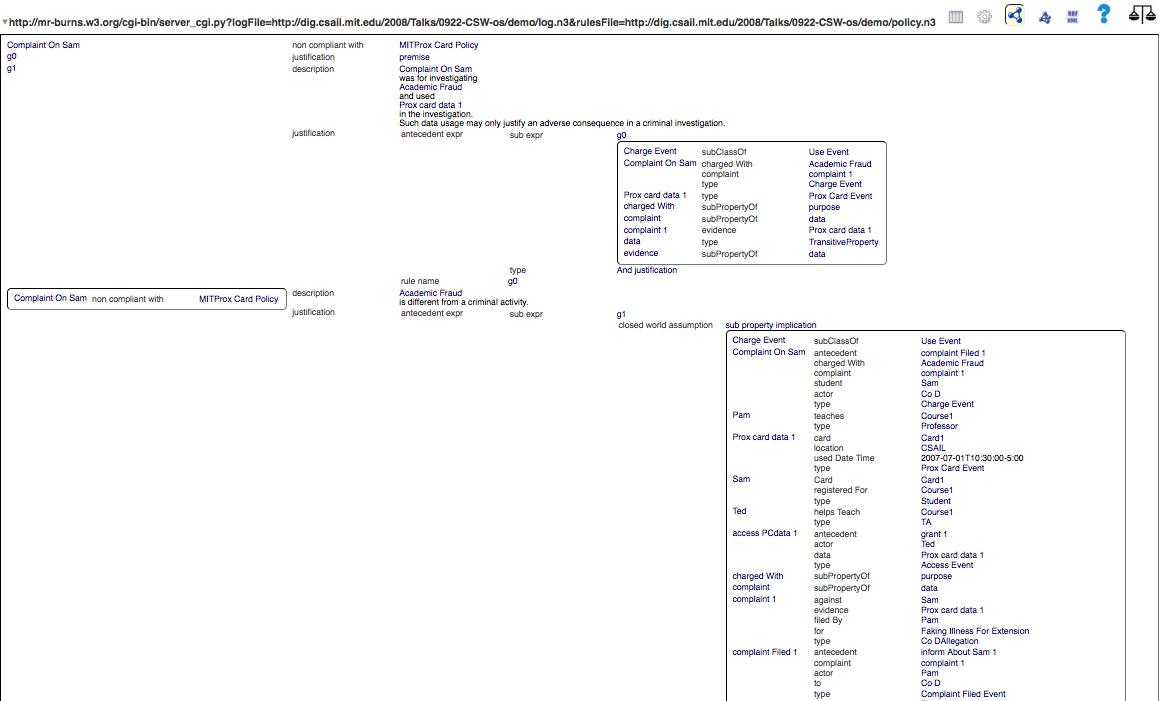
Explanations View

Explanations View
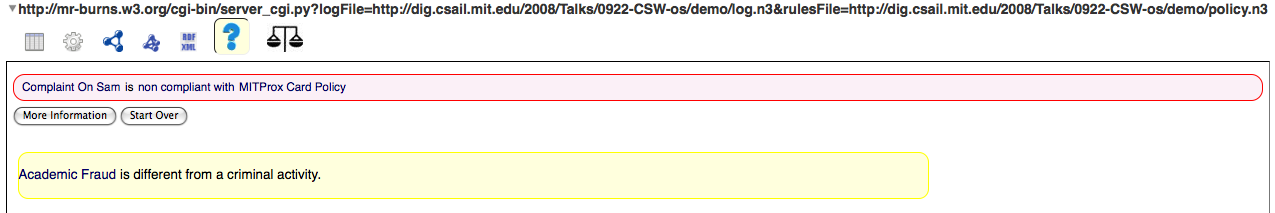
Explanations View
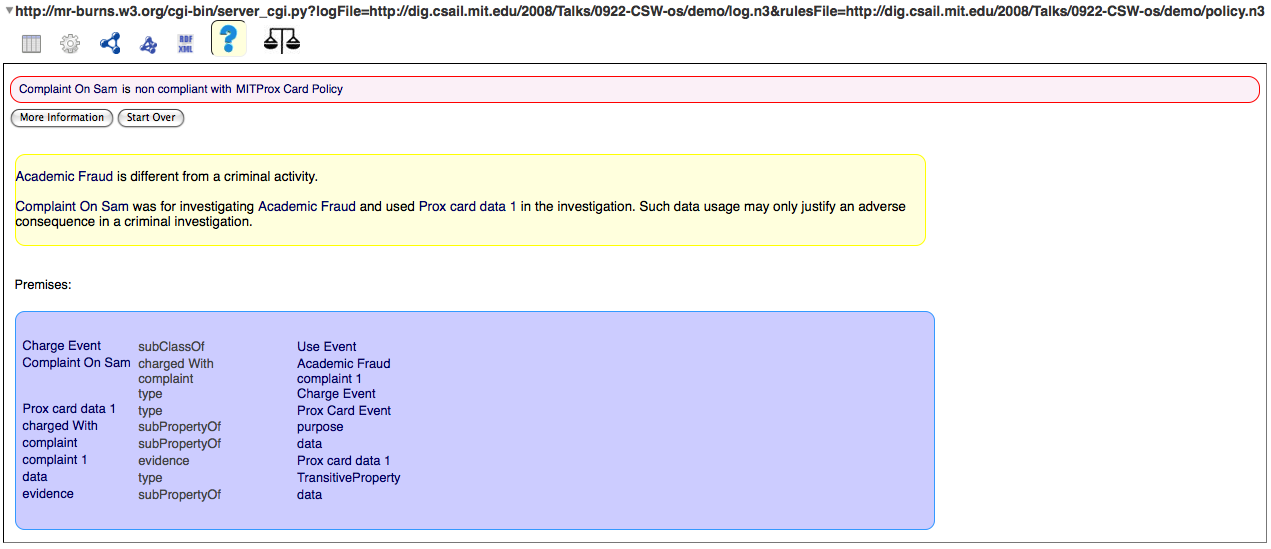
Lawyers' View
Future Plans
- Justification UI:
- Support for ontologies other than AIR
- Incorporate Transaction Log Specific Queries
- What-If-Analysis
- Tabulator:
- Integrate Policy Aware Capabilites
More Information
- This presentation: http://dig.csail.mit.edu/2008/Talks/0922-CSW-os/presentation.html
- Tabulator: Exploring and Analyzing linked data on the Semantic Web, http://swui.semanticweb.org/swui06/papers/Berners-Lee/Berners-Lee.pdf
- Tabulator Redux: Writing Into the Semantic Web http://eprints.ecs.soton.ac.uk/14773/1/tabulatorWritingTechRep.pdf
- The Point of View Axis: Varying the Levels of Explanation Within a Generic RDF Data Browsing Environment, http://dig.csail.mit.edu/2008/Papers/CSW/paper.pdf
- Using Dependency Tracking to Provide Explanations for Policy Management, http://dig.csail.mit.edu/2008/Papers/IEEE%20Policy/air-overview.pdf
- Justification UI Howto, http://dig.csail.mit.edu/TAMI/2008/JustificationUI/howto.html
- FOAF Pane on Tabulator, http://dig.csail.mit.edu/2007/tab/foaf.html










