|
|
rbac:Role a owl:Class.
rbac:ActiveRole a owl:Class.
activeForm a owl:FunctionalProperty, owl:InverseFunctionalProperty;
rdfs:domain Role;
rdfs:range ActiveRole.
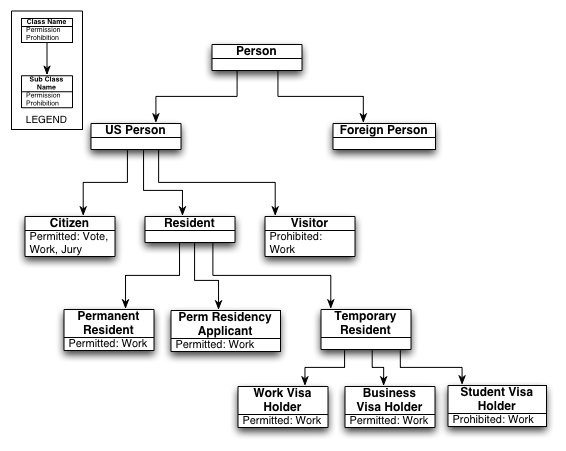
USPerson rdfs:subClassOf rbac:Role.
ActiveUSPerson rdfs:subClassOf rbac:ActiveRole,
rdfs:subClassOf USPerson.
USPerson rbac:activeForm ActiveUSPerson.
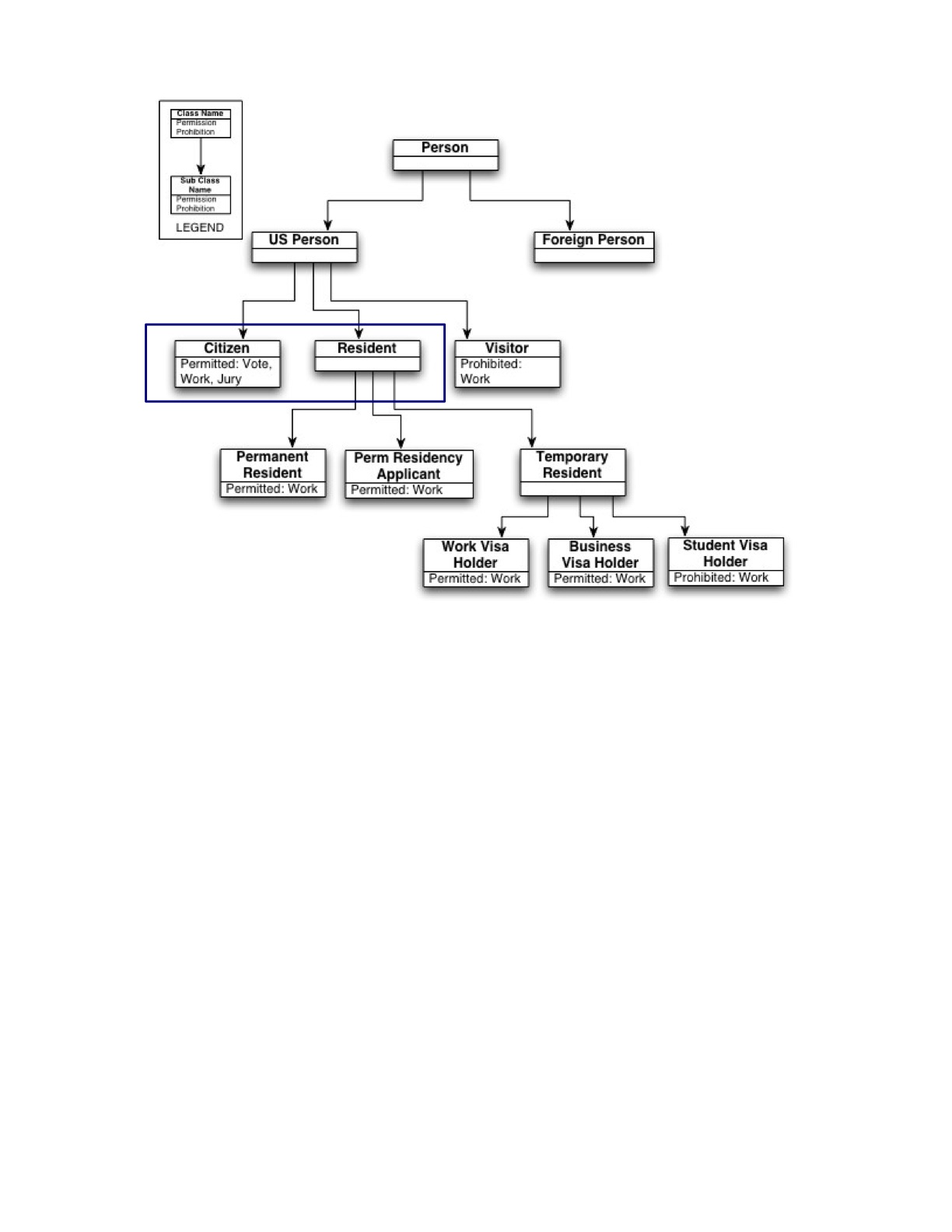
Alice a Citizen, ActiveCitizen.
Bob a Visitor, Resident.
Citizen rdfs:subclassOf USPerson.
Resident rdfs:subclassOf USPerson.
PermanentResident rdfs:subclassOf Resident.
Citizen owl:disjointWith Resident
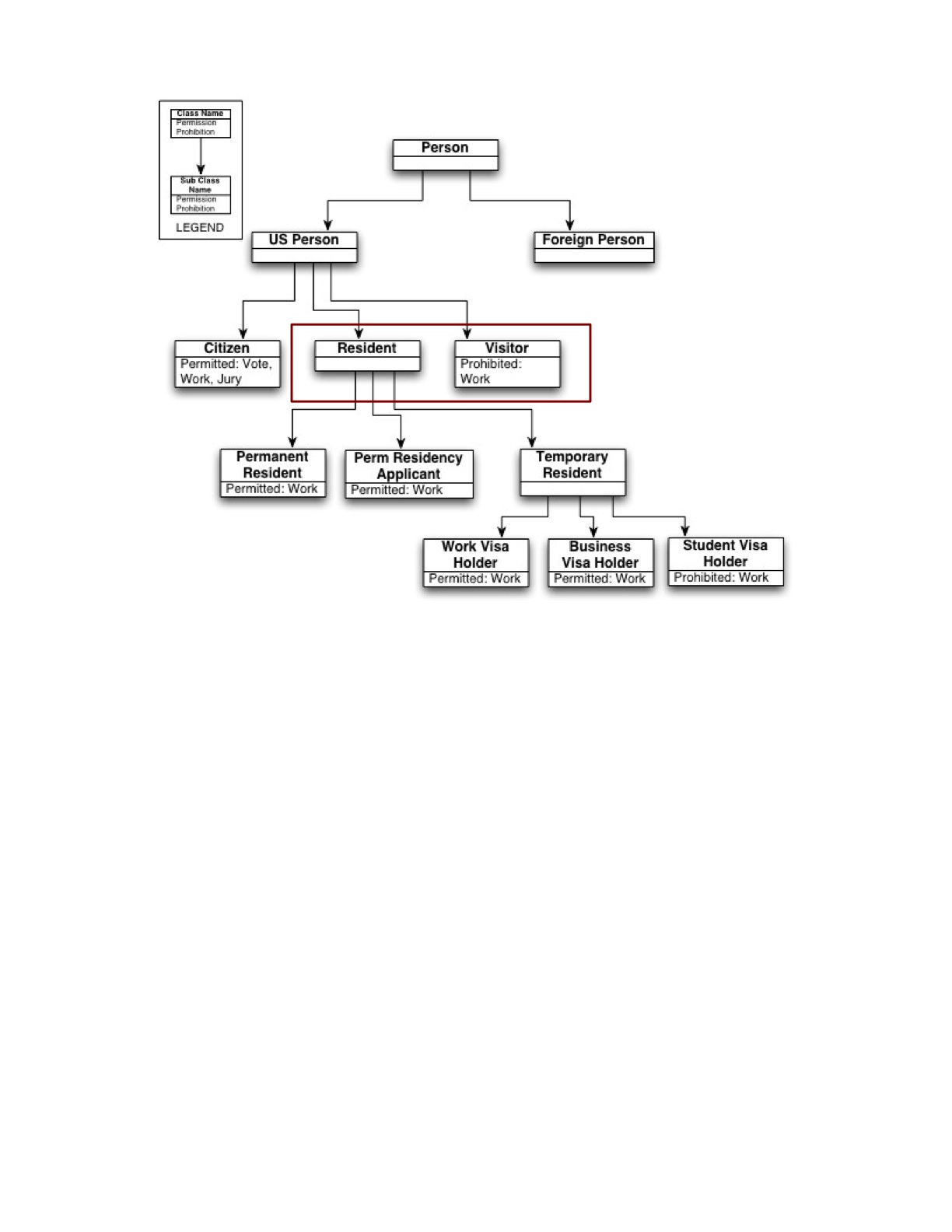
ActiveVisitor owl:disjointWith ActiveResident
PermittedVoteAction a rdfs:Class;
rdfs:subClassOf rbac:PermittedAction;
owl:equivalentClass [
a owl:Class;
owl:intersectionOf
( Vote
[ a owl:Restriction;
owl:allValuesFrom ex:ActiveCitizen;
owl:onProperty rbac:subject
]
)
] .
{ ?ACTION a ActivateRole;
subject ?SUBJ;
object ?RNEW.
?RNEW activeForm ?ARNEW.
?S a ?RCURRENT.
?RCURRENT activeForm ?ARCURRENT.
?ARNEW owl:disjointWith ?ARCURRENT.
} => {?ACTION a ProhibitedRoleActivation;
subject ?SUBJ; object ?RNEW; role ?RCURRENT;
justification "Violates DSOD constraint".}.
rbac:Role a owl:Class.
rbac:role a owl:ObjectProperty;
rdfs:domain rbac:Subject;
rdfs:range rbac:Role.
rbac:activeRole rdfs:subPropertyOf rbac:role.
USPerson a rbac:Role.
Alice rbac:role Citizen; rbac:activeRole Citizen.
Bob rbac:role Visitor, Resident.
rbac:subRole a owl:TransitiveProperty;
rdfs:domain rbac:Role;
rdfs:range rbac:Role.
Citizen rbac:subRole USPerson.
Resident rbac:subRole USPerson.
PermanentResident rbac:subRole Resident.
TemporaryResident rbac:subRole Resident
rbac:ssod a owl:SymmetricProperty, owl:TransitiveProperty;
rdfs:domain rbac:Role;
rdfs:range rbac:Role.
Resident rbac:ssod Citizen.
Visitor rbac:dsod Resident
rbac:permitted a rdfs:Property;
rdfs:domain Role;
rdfs:range Action.
Example: Citizen rbac:permitted Vote, Work, JuryDuty.
{ ?A a ?RACTION; subject ?S.
?RACTION a Action.
?ROLE permitted ?RACTION.
?S activeRole ?ROLE.
} => { ?A a PermittedAction;
role ?ROLE;
action ?RACTION;
subject ?S }.
{ ?A a rbac:Action;
rbac:subject ?S;
rbac:object ?O.
?S a UniversityPerson; office ?L,
?O a Device; location ?L.
} => { ?A a rbac:PermittedAction }.
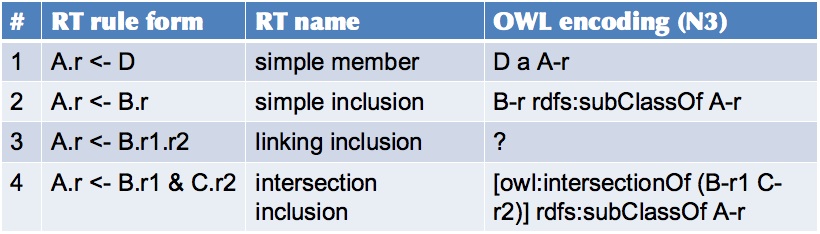
1 alice.friend <- bob ;Bob is a friend of Alice
2 alice.friend <- bob.friend ;Alice's friends include Bob's friends
3 alice.friend <- carol.enemy.enemy ;..and Carol's enemies' enemies
4 alice.friend <- umbc.student & iit.alumnus ;..and UMBC students who are IIT alumni
HQ.marketing <- HR.managers HQ.marketing <- HQ.stales HQ.marketing <- HR.sales HQ.marketing <- HQ.marketingDelg ^ HR.employee HQ.ops <- HR.managers HQ.ops <- HR.manufacturing HQ.marketingDelg <- HR.managers.access HR.employee <- HR.managers HR.employee <- HR.sales HR.employee <- HR.manufacturing HR.employee <- HR.researchDev HQ.staff <- HR.managers HQ.staff <- HQ.specialPanel ^ HR.researchDev HR.manager <- Alice HR.researchDev <- Bob Growth and shrink restricted roles: HQ.marketing, HQ.ops, HR.employee, HQ.marketingDelg, HQ.staff
